Isothermal Amplification
Isothermal amplification methods provide detection of a nucleic acid target sequence in a streamlined, exponential manner, and are not limited by the constraint of thermal cycling. Although these methods can vary considerably, they all share some features in common. For example, because the DNA strands are not heat denatured, all isothermal methods rely on an alternative approach to enable primer binding and initiation of the amplification reaction: a polymerase with strand-displacement activity. Once the reaction is initiated, the polymerase must also separate the strand that is still annealed to the sequence of interest. Isothermal amplification chemistry has been applied to diagnostics with great success and is utilized in several commercial molecular diagnostic platforms, serving large testing centers and point-of-care markets.
The COVID-19 pandemic has seen isothermal methods being adopted as the foundational technology used to detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the clinical and home testing market. Two examples of colorimetric LAMP in COVID-19 diagnostics can be seen in the Color Genomics SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostic Assay and NEB’s internal CLIA-certified onsite testing program utilizing saliva. Recent preprints and publications communicate the utility of isothermal amplification methods such as NASBA and RTF-EXPAR in this area:
- INSIGHT: A population-scale COVID-19 testing strategy combining point-of-care diagnosis with centralized high-throughput sequencing
- Sub-5-minute Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using a Reverse Transcriptase-Free Exponential Amplification Reaction, RTF-EXPAR
Isothermal methods typically employ unique DNA polymerases for separating duplex DNA. DNA polymerases with this ability include Klenow exo-, Bsu large fragment, and phi29 for moderate temperature reactions (25–40°C) and the large fragment of Bst DNA polymerase for higher temperature (50–65°C) reactions. To detect RNA species, a reverse transcriptase compatible with the temperature of the reaction is added (except in the NASBA/TMA reaction) to maintain the isothermal nature of the amplification.
Isothermal DNA Amplification Technologies
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
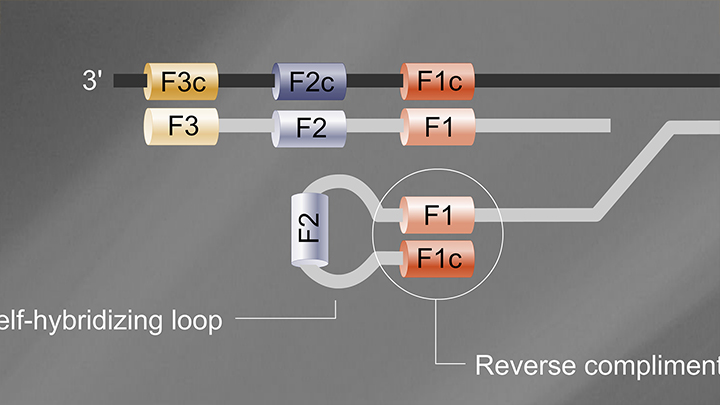
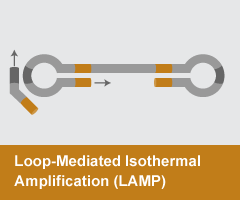
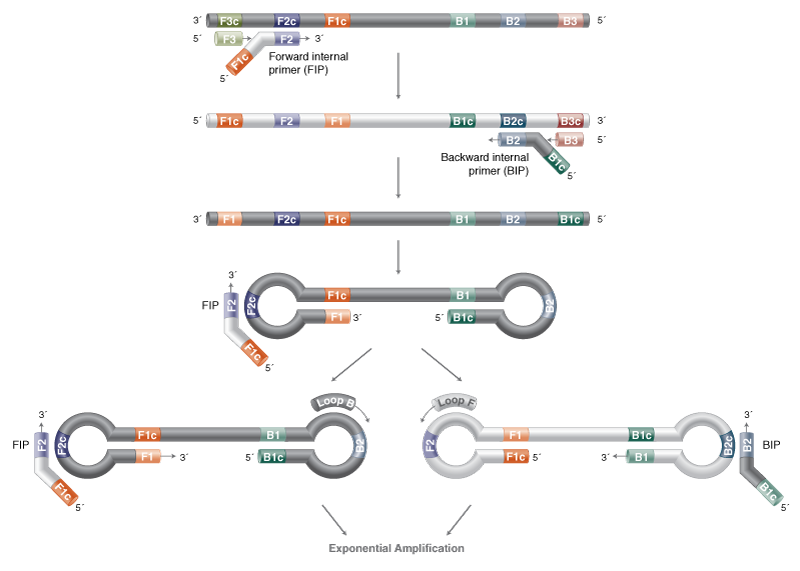
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
- Reaction temperature: 65°C
- Amplicon size: <250 nt
- DNA product: long, branched
LAMP is compatible with multiple detection methods via the WarmStart® Multi-Purpose LAMP/RT-LAMP 2X Master Mix (with UDG). For fluorescent detection to support high-throughput testing workflows, the WarmStart Fluorescent LAMP/RT-LAMP Kit (with UDG) is recommended. Colorimetric detection by changes in pH is enabled by the WarmStart Colorimetric LAMP 2X Master Mix with UDG.
LAMP primers can be challenging to design manually, and software programs are strongly recommended for both ease of design and likelihood of reaction success. We recommend using the NEB LAMP Primer Design Tool.
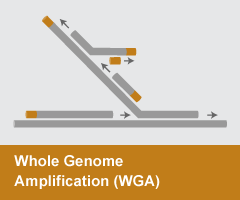
Whole Genome Amplification (WGA)
- Reaction temperature: 30°C
- Amplicon size: N/A
- DNA product: long, branched
WGA is a method of Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) that utilizes the strand-displacement activity of DNA polymerases such as phi29 or Bst DNA Polymerase to enable robust amplification of an entire genome. WGA has become an invaluable approach for utilizing limited samples of precious stock material or to enable sequencing of single-cell genomic DNA. Products of the reaction are extremely long (>30 kb) and highly branched through the multiple displacement mechanism.
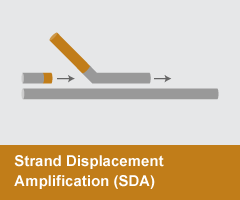
Strand Displacement Amplification (SDA)
- Reaction temperature: 60°C
- Amplicon size: <100 nt
- DNA product: short, discrete
SDA, or a similar approach, Nicking Enzyme Amplification Reaction (NEAR), relies on a strand-displacing DNA polymerase, typically Bst DNA Polymerase, Large Fragment or Klenow Fragment (3’-5’ exo–), to initiate at nicks created by a strand-limited restriction endonuclease or nicking enzyme at a site contained in a primer. The nicking site is regenerated with each polymerase displacement step, resulting in exponential amplification. NEAR is extremely rapid and sensitive, enabling detection of small target amounts in minutes. SDA and NEAR are typically utilized in clinical and biosafety applications.
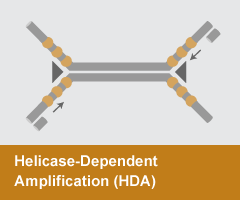
Helicase-Dependent Amplification (HDA)
- Reaction temperature: 65°C
- Amplicon size: <150 nt
- DNA product: short, discrete
HDA employs the double-stranded DNA unwinding activity of a helicase to separate strands, enabling primer annealing and extension by a strand-displacing DNA polymerase. Like PCR, this system requires only two primers. HDA has been employed in several diagnostic devices and FDA-approved tests.
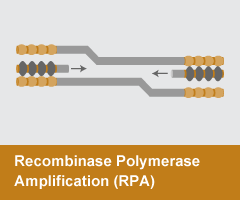
Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA)
- Reaction temperature: 37°C
- Amplicon size: <1,000 nt
- DNA product: short, discrete
RPAuses a recombinase enzyme to help primers invade double-stranded DNA. T4 UvsX, UvsY, and a single stranded binding protein T4 gp32 form D-loop recombination structures that initiate amplification by a strand-displacing DNA polymerase. RPA is typically performed at ~37 °C and, unlike other methods, can produce discrete amplicons up to 1 kb.
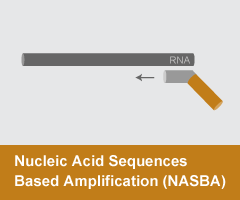
Nucleic Acid Sequences Based Amplification (NASBA)
- Reaction temperature: 40-55°C
- Amplicon size: <150 nt
- DNA product: short, discrete
NASBAand Transcription Mediated Amplification (TMA) are both isothermal amplification methods that proceed through RNA. Primers are designed to target a region of interest; one of the primers must include the promoter sequence for T7 RNA polymerase at the 5’ end. NASBA and TMA reactions are utilized in a range of clinical diagnostics.
Choose Type:
- Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification
- Whole Genome Amplification & Multiple Displacement Amplification
- Strand Displacement Amplification & Nicking Enzyme Amplification Reaction
- Helicase-dependent Amplification
- Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and SIBA
- Nucleic Acid Sequenced Based Amplification and Transcription Mediated Amplification
- One-Step qHDA (Real-time quantitative tHDA)
- One-Step qRT-HDA (Real-time quantitative RT-HDA)
- One-Step RT-HDA (Reverse Transcription tHDA)
- One-Step tHDA (thermostable HDA)
- Two-Step qHDA (Real-time quantitative tHDA)
- Two-Step qRT-HDA (Real-time quantitative RT-HDA)
- Two-Step RT-HDA (Reverse Transcription tHDA)
- Two-Step tHDA (thermostable HDA)
- Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
- Typical cDNA Synthesis Protocol with WarmStart RTx (NEB #M0380)
- Typical RT-LAMP Protocol
- Typical LAMP Protocol (M0275)
- Typical LAMP Protocol (M0537)
- Typical LAMP Protocol (M0538)
- Typical LAMP Protocol (M0374)
- WarmStart Colorimetric LAMP 2X Master Mix Typical LAMP Protocol (M1800)
- WarmStart LAMP Kit (DNA & RNA) Protocol (E1700)
-
Anatomy of a Polymerase - How Function and Structure are Related
Read about the relationship between Polymerase structure and function when copying DNA.
-
Using aptamers to control enzyme activity: Hot Start Taq and beyond
This article describes the use of engineered oligonucleotides known as aptamers in regulating the enzyme activity of polymerases and reverse transcriptases.
-
Many Initiatives Turning to RT-LAMP as Alternative to PCR for Rapid COVID-19 Screening Assays
There is an increasing demand for large-scale screening and surveillance testing, teams are now scaling up rapid SARS-CoV-2 screening assays incorporating RT-LAMP.
-
BMG LABTECH: LAMP assay for detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA using an absorbance-based colorimetric readout
There is an increasing demand for large-scale screening and surveillance testing, teams are now scaling up rapid SARS-CoV-2 screening assays incorporating RT-LAMP.
-
Mitigating Risk and Ensuring Consistent Supply Chain Through Internal SARS-CoV-2 Testing with RT-LAMP
This feature article describes how NEB scientists established a CLIA-certified SARS-CoV-2 onsite testing program utilizing saliva and colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)
- Isothermal Amplification Brochure
Feature Articles
Brochures
- Zhang M, Ye J, He JS, et al. (2020) Visual detection for nucleic acid-based techniques as potential on-site detection methods. A review. Anal Chim Acta; 1099:1–15, PubMedID: 31986265, DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2019.11.056
- Poole, C.B., Sinha, A., Ettwiller, L., Apone, L., McKay, K., Panchapakesa, V., Lima, N.F., Ferreira, M.U., Wanji, S., Carlow, C.K.S (2019) In silico identification of novel biomarkers and development of new rapid diagnostic tests for the filarial parasites Mansonella perstans and Mansonella ozzardi Sci Rep; 9 (1), 10275. PubMedID: 31311985, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46550-9
- Nzelu CO, Kato H, Peters NC. (2019) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): An advanced molecular point-of-care technique for the detection of Leishmania infection PLoS Negl Trop Dis; 13(11):e0007698, PubMedID: 31697673, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007698
- Toldrà A, O'Sullivan CK, Campàs M. (2019) Detecting Harmful Algal Blooms with Isothermal Molecular Strategies Trends Biotechnol; 37(12):1278–1281, PubMedID: 31399265, DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2019.07.003
- Mao D , Chen T , Chen H , et al. (2019) pH-Based immunoassay: explosive generation of hydrogen ions through an immuno-triggered nucleic acid exponential amplification reaction Analyst; 144(13):4060–4065, PubMedID: 31165121, DOI: 10.1039/c9an00506d
- Calvert AE, Biggerstaff BJ, Tanner NA, Lauterbach M, Lanciotti RS. (2017) Rapid colorimetric detection of Zika virus from serum and urine specimens by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) PLoS One; 12(9):e0185340, PubMedID: 28945787, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185340
- Schoepp NG, Schlappi TS, Curtis MS, et al. (2017) Rapid pathogen-specific phenotypic antibiotic susceptibility testing using digital LAMP quantification in clinical samples Sci Transl Med; 9(410):eaal3693, PubMedID: 28978750, DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3693
- Tanner NA, Evans TC Jr. (2014) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of nucleic acids Curr Protoc Mol Biol; 105, PubMedID: 24510439
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.